Search Results for: resting cells
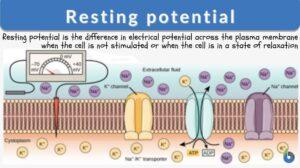
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
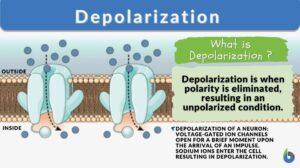
Depolarization
Depolarization is the removal of polarity by a process or action. It might also be used to describe how such activity leads... Read More
Generation of resting membrane potential
Stephen H. Wright Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85724... Read More
Resting cells
resting cell A quiescent cell; one not undergoing... Read More
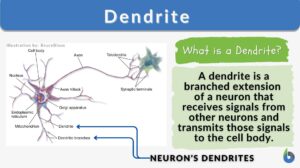
Neural Control Mechanisms
Nerve cells called neurons generate electric signals that pass from one end of the cell to another and release chemical... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
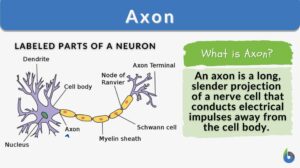
Axon hillock
Axon Hillock Definition What is axon hillock? If you are familiar with the different parts of the neuron, the axon hillock... Read More
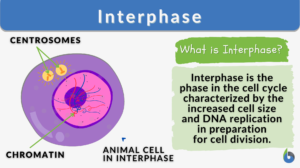
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
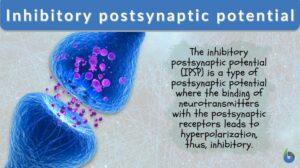
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential Definition An inhibitory postsynaptic potential is a type of synaptic potential. It is... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Sarcolemma
Sarcolemma Definition What is the sarcolemma? It is the thin, transparent, extensible plasma membrane of the muscle cell.... Read More
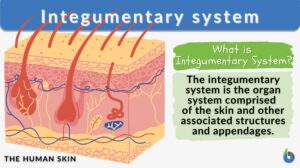
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis Definition Phagocytosis is a basic physiological cellular process wherein a cell ingests a solid particle... Read More
Gap 0 phase
Definition noun The phase in the cell cycle wherein the cell is in inactive or non-cycling state following cell... Read More
Sensory Systems
A sensory system is a part of the nervous system consisting of sensory receptors that receive stimuli from the internal and... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
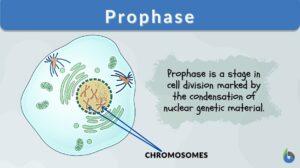
Cell cycle
Definition noun (cell biology) The sequence of growth and division of a cell, and consists of a series of biological... Read More
Microelectrode
Definition noun, plural: microelectrodes An electrode with a tip having dimensions of the order of one micrometer, thereby... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Interkinesis
Definition noun Interphase II, i.e. a short resting period occurring between meiosis I and meiosis II Supplement Meiosis is... Read More
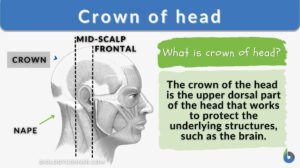
Crown of head
Crown of Head Definition The crown of the head is the upper dorsal part (or area) of the head. Several creatures have... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
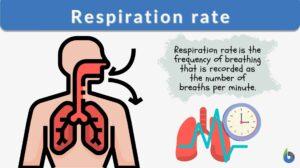
Respiration rate
Respiration Rate Definition Respiration rate is a vital life process that expresses the breathing rate in an organism... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
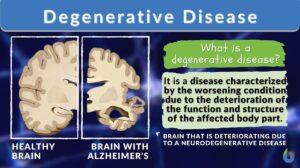
Degenerative disease
Degenerative Disease Definition A degenerative disease is defined as a disease characterized by the worsening condition due... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
Dinoflagellate
A dinoflagellate is a flagellate algae characterized by their two flagella of unequal length. One of the flagella is lying... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Unstriated muscle
unstriated muscle --> smooth muscle (Science: anatomy, pathology, physiology) muscle tissue in vertebrates made up from... Read More
Mitotic phase
Definition noun The phase in the life cycle of a cell highlighted by chromosomal separation resulting into two identical... Read More
Gap 2 phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase of the cell cycle wherein the cell continues to grow and then... Read More